
A strong conceptual framework underpins good research. A conceptual framework in research is used to understand a research problem and guide the development and analysis of the research. It serves as a roadmap to conceptualize and structure the work by providing an outline that connects different ideas, concepts, and theories within the field of study. A conceptual framework pictorially or verbally depicts presumed relationships among the study variables.
The purpose of a conceptual framework is to serve as a scheme for organizing and categorizing knowledge and thereby help researchers in developing theories and hypotheses and conducting empirical studies.
In this post, we explain what is a conceptual framework, and provide expert advice on how to make a conceptual framework, along with conceptual framework examples.
What is a Conceptual Framework in Research
Definition of a Conceptual Framework
A conceptual framework includes key concepts, variables, relationships, and assumptions that guide the academic inquiry. It establishes the theoretical underpinnings and provides a lens through which researchers can analyze and interpret data. A conceptual framework draws upon existing theories, models, or established bodies of knowledge to provide a structure for understanding the research problem. It defines the scope of research, identifying relevant variables, establishing research questions, and guiding the selection of appropriate methodologies and data analysis techniques.
Conceptual frameworks can be written or visual. Other types of conceptual framework representations might be taxonomic (verbal description categorizing phenomena into classes without showing relationships between classes) or mathematical descriptions (expression of phenomena in the form of mathematical equations).
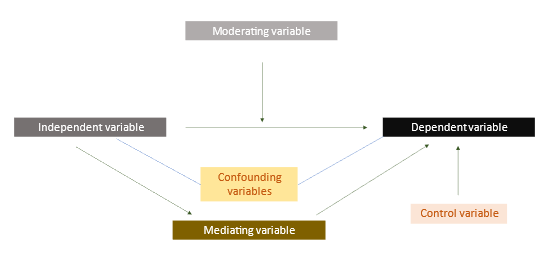
Figure 1: Definition of a conceptual framework explained diagrammatically
Conceptual Framework Origin
The term conceptual framework appears to have originated in philosophy and systems theory, being used for the first time in the 1930s by the philosopher Alfred North Whitehead. He bridged the theological, social, and physical sciences by providing a common conceptual framework. The use of the conceptual framework began early in accountancy and can be traced back to publications by William A. Paton and John B. Canning in the first quarter of the 20th century. Thus, in the original framework, financial issues were addressed, such as useful features, basic elements, and variables needed to prepare financial statements. Nevertheless, a conceptual framework approach should be considered when starting your research journey in any field, from finance to social sciences to applied sciences.
 Purpose and Importance of a Conceptual Framework in Research
Purpose and Importance of a Conceptual Framework in Research
The importance of a conceptual framework in research cannot be understated, irrespective of the field of study. It is important for the following reasons:
- It clarifies the context of the study.
- It justifies the study to the reader.
- It helps you check your own understanding of the problem and the need for the study.
- It illustrates the expected relationship between the variables and defines the objectives for the research.
- It helps further refine the study objectives and choose the methods appropriate to meet them.
What to Include in a Conceptual Framework
Essential elements that a conceptual framework should include are as follows:
- Overarching research question(s)
- Study parameters
- Study variables
- Potential relationships between those variables.
The sources for these elements of a conceptual framework are literature, theory, and experience or prior knowledge.
How to Make a Conceptual Framework
Now that you know the essential elements, your next question will be how to make a conceptual framework.
For this, start by identifying the most suitable set of questions that your research aims to answer. Next, categorize the various variables. Finally, perform a rigorous analysis of the collected data and compile the final results to establish connections between the variables.
In short, the steps are as follows:
- Choose appropriate research questions.
- Define the different types of variables involved.
- Determine the cause-and-effect relationships.
Be sure to make use of arrows and lines to depict the presence or absence of correlational linkages among the variables.
Developing a Conceptual Framework
Researchers should be adept at developing a conceptual framework. Here are the steps for developing a conceptual framework:
1. Identify a research question
Your research question guides your entire study, making it imperative to invest time and effort in formulating a question that aligns with your research goals and contributes to the existing body of knowledge. This step involves the following:
- Choose a broad topic of interest
- Conduct background research
- Narrow down the focus
- Define your goals
- Make it specific and answerable
- Consider significance and novelty
- Seek feedback.
2. Choose independent and dependent variables
The dependent variable is the main outcome you want to measure, explain, or predict in your study. It should be a variable that can be observed, measured, or assessed quantitatively or qualitatively. Independent variables are the factors or variables that may influence, explain, or predict changes in the dependent variable.
Choose independent and dependent variables for your study according to the research objectives, the nature of the phenomenon being studied, and the specific research design. The identification of variables is rooted in existing literature, theories, or your own observations.
3. Consider cause-and-effect relationships
To better understand and communicate the relationships between variables in your study, cause-and-effect relationships need to be visualized. This can be done by using path diagrams, cause-and-effect matrices, time series plots, scatter plots, bar charts, or heatmaps.
4. Identify other influencing variables
Besides the independent and dependent variables, researchers must understand and consider the following types of variables:
- Moderating variable: A variable that influences the strength or direction of the relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable.
- Mediating variable: A variable that explains the relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable and clarifies how the independent variable affects the dependent variable.
- Control variable: A variable that is kept constant or controlled to avoid the influence of other factors that may affect the relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
- Confounding variable: A type of unmeasured variable that is related to both the independent and dependent variables.
Example of a Conceptual Framework
Let us examine the following conceptual framework example. Let’s say your research topic is “The Impact of Social Media Usage on Academic Performance among College Students.” Here, you want to investigate how social media usage affects academic performance in college students. Social media usage (encompassing frequency of social media use, time spent on social media platforms, and types of social media platforms used) is the independent variable, and academic performance (covering grades, exam scores, and class attendance) is the dependent variable.
This conceptual framework example also includes a mediating variable, study habits, which may explain how social media usage affects academic performance. Study habits (time spent studying, study environment, and use of study aids or resources) can act as a mechanism through which social media usage influences academic outcomes. Additionally, a moderating variable, self-discipline (level of self-control and self-regulation, ability to manage distractions, and prioritization skills), is included to examine how individual differences in self-control and discipline may influence the relationship between social media usage and academic performance.
Confounding variables are also identified (socioeconomic status, prior academic achievement), which are potential factors that may influence both social media usage and academic performance. These variables need to be considered and controlled in the study to ensure that any observed effects are specifically attributed to social media usage. A visual representation of this conceptual framework example is seen in Figure 2.
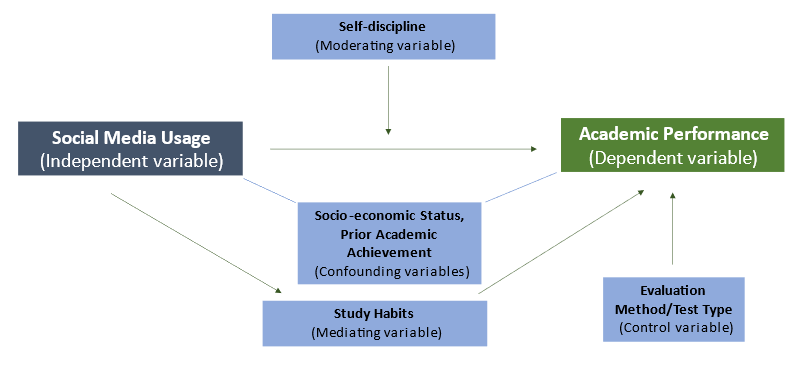
Figure 2: Visual representation of a conceptual framework for the topic “The Impact of Social Media Usage on Academic Performance among College Students”
Key Takeaways
Here is a snapshot of the basics of a conceptual framework in research:
- A conceptual framework is an idea or model representing the subject or phenomena you intend to study.
- It is primarily a researcher’s perception of the research problem. It can be used to develop hypotheses or testable research questions.
- It provides a preliminary understanding of the factors at play, their interrelationships, and the underlying reasons.
- It guides your research by aiding in the formulation of meaningful research questions, selection of appropriate methods, and identification of potential challenges to the validity of your findings.
- It provides a structure for organizing and understanding data.
- It allows you to chalk out the relationships between concepts and variables to understand them.
- Variables besides dependent and independent variables (moderating, mediating, control, and confounding variables) must be considered when developing a conceptual framework.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a moderating variable and a mediating variable?
Moderating and mediating variables are easily confused. A moderating variable affects the direction and strength of this relationship, whereas a mediating explains how two variables relate.
What is the difference between independent variables, dependent variables, and confounding variables?
Independent variables are the variables manipulated to affect the outcome of an experiment (e.g., the dose of a fat-loss drug administered to rats). Dependent variables are variables being measured or observed in an experiment (e.g., changes in rat body weight as a result of the drug). A confounding variable distorts or masks the effects of the variables being studied because it is associated both with dependent variable and with the independent variable. For instance, in this example, pre-existing metabolic dysfunction in some rats could interact differently with the drug being studied and also affect rat body weight.
Should I have more than one dependent or independent variable in a study?
The need for more than one dependent or independent variable in a study depends on the research question, study design, and relationships being investigated. Note the following when making this decision for your research:
- If your research question involves exploring the relationships between multiple variables or factors, it may be appropriate to have more than one dependent or independent variable.
- If you have specific hypotheses about the relationships between several variables, it may be necessary to include multiple dependent or independent variables.
- Adequate resources, sample size, and data collection methods should be considered when determining the number of dependent and independent variables to include.
What is a confounding variable?
A confounding variable is not the main focus of the study but can unintentionally influence the relationship between the independent and dependent variables. Confounding variables can introduce bias and give rise to misleading conclusions. These variables must be controlled to ensure that any observed relationship is genuinely due to the independent variable.
What is a control variable?
A control variable is something not of interest to the study’s objectives but is kept constant because it could influence the outcomes. Control variables can help prevent research biases and allow for a more accurate assessment of the relationship between the independent and dependent variables. Examples are (i) testing all participants at the same time (e.g., in the morning) to minimize the potential effects of circadian rhythms, (ii) ensuring that instruments are calibrated consistently before each measurement to minimize the influence of measurement errors, and (iii) randomization of participants across study groups.
R Discovery is a literature search and research reading platform that accelerates your research discovery journey by keeping you updated on the latest, most relevant scholarly content. With 250M+ research articles sourced from trusted aggregators like CrossRef, Unpaywall, PubMed, PubMed Central, Open Alex and top publishing houses like Springer Nature, JAMA, IOP, Taylor & Francis, NEJM, BMJ, Karger, SAGE, Emerald Publishing and more, R Discovery puts a world of research at your fingertips.
Try R Discovery Prime FREE for 1 week or upgrade at just US$72 a year to access premium features that let you listen to research on the go, read in your language, collaborate with peers, auto sync with reference managers, and much more. Choose a simpler, smarter way to find and read research – Download the app and start your free 7-day trial today!



